AWS S3
Store your builds in AWS S3
This feature is available to users on our Pro plan and up.
Introduction
While Buildstash offers simple, low-cost storage for your builds out the box, you may prefer to host your own build data. We make it easy to connect an AWS S3 bucket (or S3 API compatible storage from another provider).
Follow the steps below to setup a custom storage bucket on an application.
Prepare S3 bucket
If you haven't already created an S3 bucket to use with Buildstash, it is strongly advised to start with a new or empty bucket. Our application expects a certain directory structure and won't be able to work with existing files.
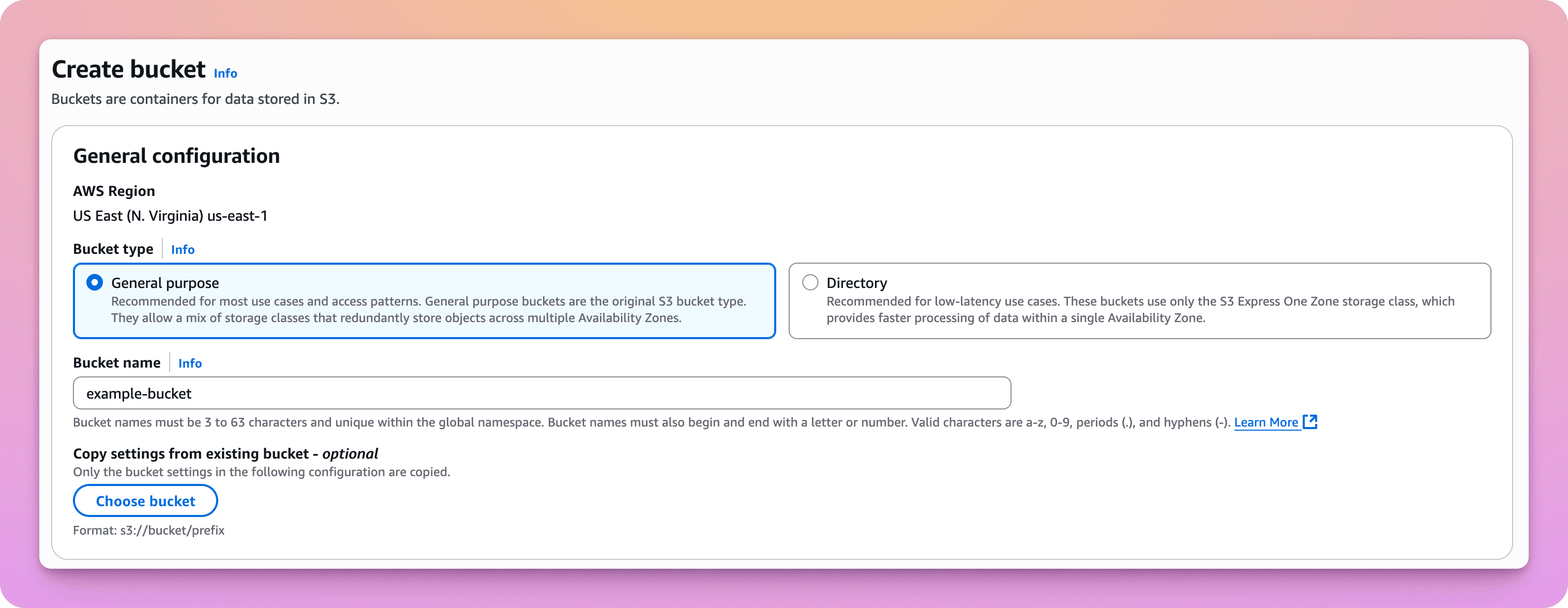
Once you've connected a bucket to Buildstash, you can feel free to re-use across applications (or even workspaces) as you prefer.
You can disable ACLs, and block all public access during creation.
Once the bucket is created, you must set your CORS policy to allow Buildstash domains the access we need.
To edit the bucket's CORS policy, select your bucket in the AWS console, then go to Permissions > Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) > Edit.
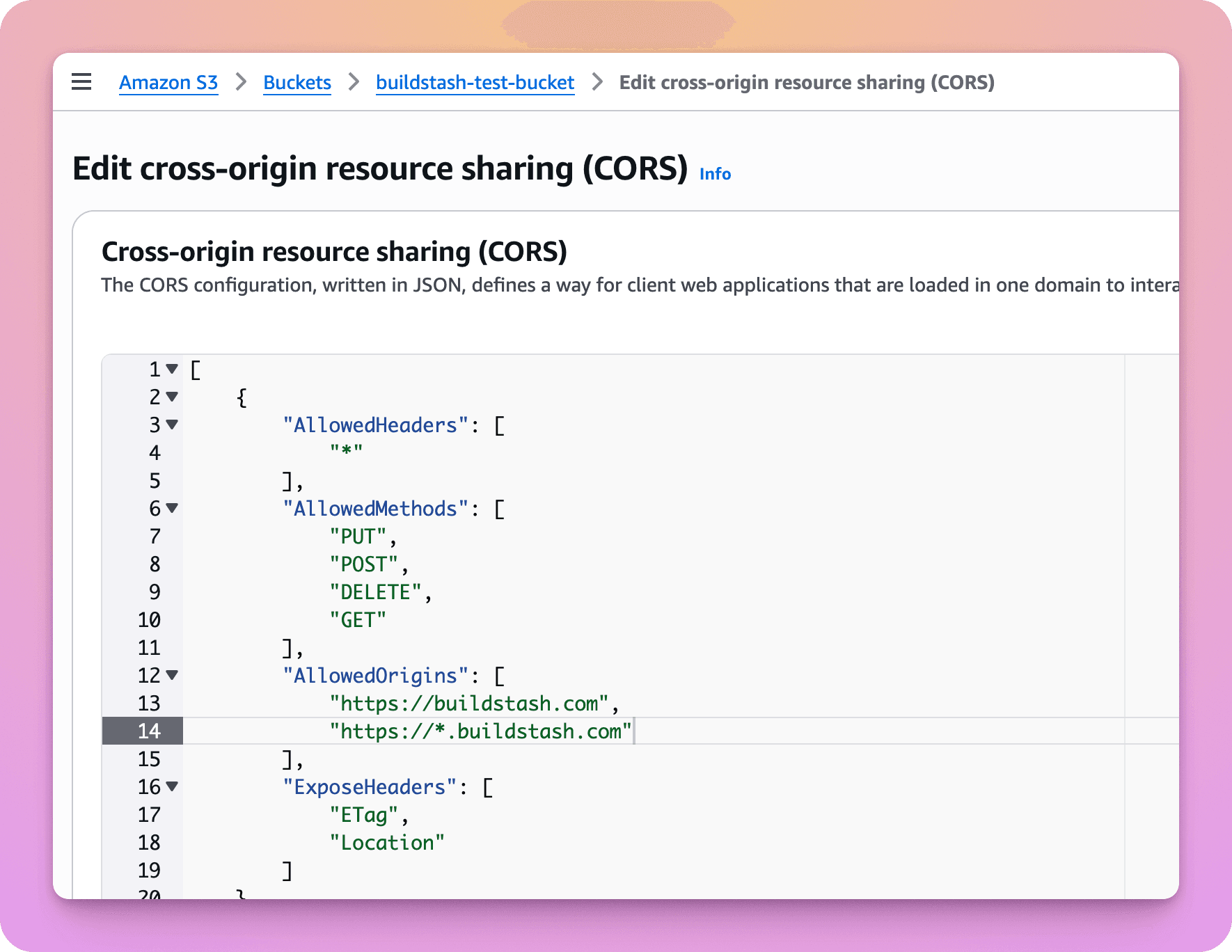
[
{
"AllowedHeaders": [
"*"
],
"AllowedMethods": [
"PUT",
"POST",
"DELETE",
"GET"
],
"AllowedOrigins": [
"https://buildstash.com",
"https://*.buildstash.com",
"https://builds.download",
"https://*.builds.download",
"https://buildsta.sh",
"https://*.buildsta.sh"
],
"ExposeHeaders": [
"ETag",
"Location"
]
}
]Enter the above JSON configuration, then save.
You'll need to create an IAM user in AWS with the necessary access to your new bucket.
You can follow the instructions in the AWS documentation to set this up, and create an access key for the user. We recommend creating a user specifically for this purpose, locked down with just the necessary access to this bucket.
Below is an example of a valid access policy, assuming your bucket was titled "buildstash-builds-bucket".
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:ListBucket",
"s3:ListBucketMultipartUploads",
"s3:GetBucketCORS",
"s3:GetBucketLocation",
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:GetObjectAcl",
"s3:PutObject",
"s3:DeleteObject",
"s3:ListMultipartUploadParts",
"s3:AbortMultipartUpload",
"s3:RestoreObject",
"s3:ReplicateObject"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::buildstash-builds-bucket",
"arn:aws:s3:::buildstash-builds-bucket/*"
]}
]
}Securely note the access key and secret access key provided.
Connect bucket to your Buildstash app
In a fresh Buildstash application, go into your app's Settings > Storage > Configure storage.
Note, you can only setup custom storage on an application when no builds are stored in it. This also applies to removing an existing custom store and switching back to Buildstash provided storage.
Enter the details for your S3 bucket, including the correct bucket region.
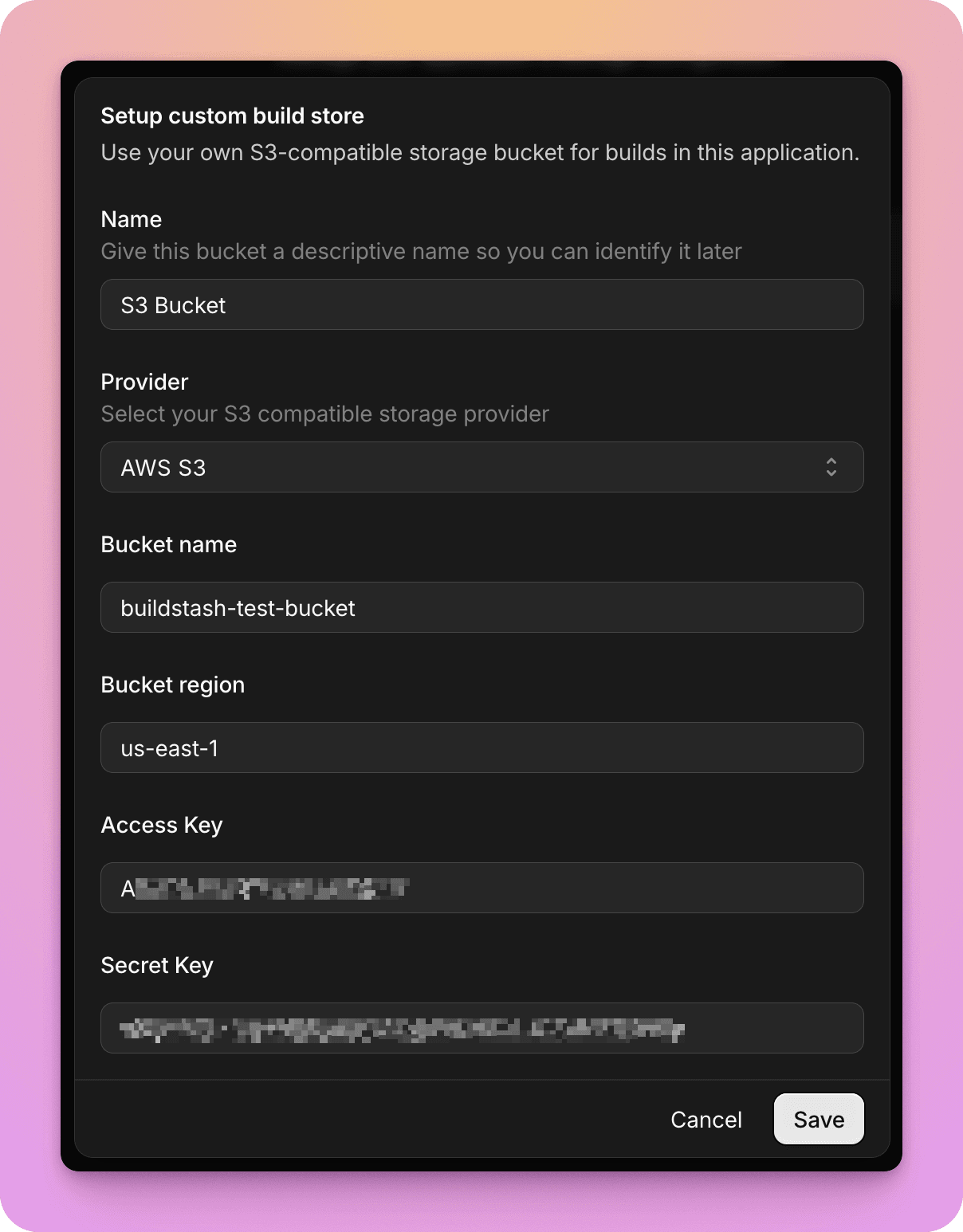
When you hit "Save" a test connection request will be made to the bucket, and if it is successful, the custom store will successfully save.
Builds uploaded to this application will now be hosted within your custom bucket.
Buildstash now expects to manage the files in this bucket, and that files will be where we expect them to be.
Please manage build files (uploading, deleting, etc) via the Buildstash interface and our provided tooling, and don't edit files directly in the bucket, to avoid causing issues like broken build links.